接上文的react项目的render模板合并冲突检测插件发布之后,今天这篇主要讲如何实现vue的合并冲突检测webpack插件
前面react的文章实现了如何在打包模式下检测render模板中是否有遗留的合并冲突代码。vue也可以吗?
答案是肯定的!只是实现的思路以及方法从babel插件变为了webpack插件。
为啥之前的babel插件实现不行了
上偏文章说过了,react中的jsx其实最终都是会被babel编译成react.createElement的形式,因此我们可以通过babel插件的形式对react的渲染模板进行ast语法树的分析。
那么vue呢?在astexplore网站中我们选择编译的文件类型是vue就可以看到vue单文件编译成的ast语法树结构。

那么我们也可以利用这种形式来编写一个babel插件的形式来对vue中的template进行ast语法树的分析?事实上并不行,经由webpack进行打包的vue项目类似于vue-cli,webpack并不能识别.vue文件结尾的单文件。所以vue中的.vue单文件首先要经过vue-loader进行处理,在vue-loader中,会通过官方的vue-template-compilre进行编译静态分析优化等操作。其中的script代码任然会交给babel进行处理编译,但是template渲染模板会由vue-template-compilre进行编译优化生成成最终的字符串模板。
啥意思呢,就是.vue文件中的template变异之后的代码并不会再交给babel进行处理,vue-template-compilre已经干完了这些事情了。所以想通过babel插件的形式获取到template编译后的代码是拿不到的。
换个思路-webpack插件
既然babel插件的方式行不通那就要换个思路了: 我们知道的是不管template中的代码怎么折腾,最终渲染模板代码都会被webpack打包成一个module模块,再交由webpack拼装组合优化等操作输出成js文件。
所以,我们可以通过webpack插件监听特定的生命周期钩子,获取到打包时候生成的module模块。经过一些筛选比对这样子就能获取到vue-template-compilre编译之后的渲染模板代码。
本文并不是来教你怎么写一个wenpack插件的,webpack插件的相关还是可以移步去webpack官网恶补一下。
为了获取到被webpack生成的完整module,我们监听compilation的seal钩子即可:
从webpack生成的modules中查找template模块
class CheckVueConflictPlugin {
private readonly options: CheckVueConflictPluginOptions;
constructor(options?: CheckVueConflictPluginOptions) {
this.options = options || {};
}
apply(compiler: Compiler) {
const { force = false } = this.options;
const pluginName = this.constructor.name;
const { options } = compiler;
const { mode } = options;
// 非生产模式并且不需要强制执行直接退出即可
if (mode !== 'production' && !force) {
return;
}
// 注册实例化compilation之后的钩子
compiler.hooks.compilation.tap(pluginName, (compilation) => {
compilation.hooks.seal.tap(pluginName, () => {
const newModule = Array.from(compilation.modules) as VueTemplateModule[];
// 筛选出type为template的渲染模板module
const templateModulesArray = newModule.filter(
(module) => module.resource && isVueTemplate(module.resource) && module.resource !== module.userRequest,
);
});
});
}
}
.vue单文件经过vue-template-compilre编译后会被拆分成三个文件,通过type来区分:
source.vue?vue&type=template表示渲染函数模板source.vue?vue&type=script表示script中的js逻辑source.vue?vue&type=style表示样式文件
看一下webpack打包的template渲染函数模块:
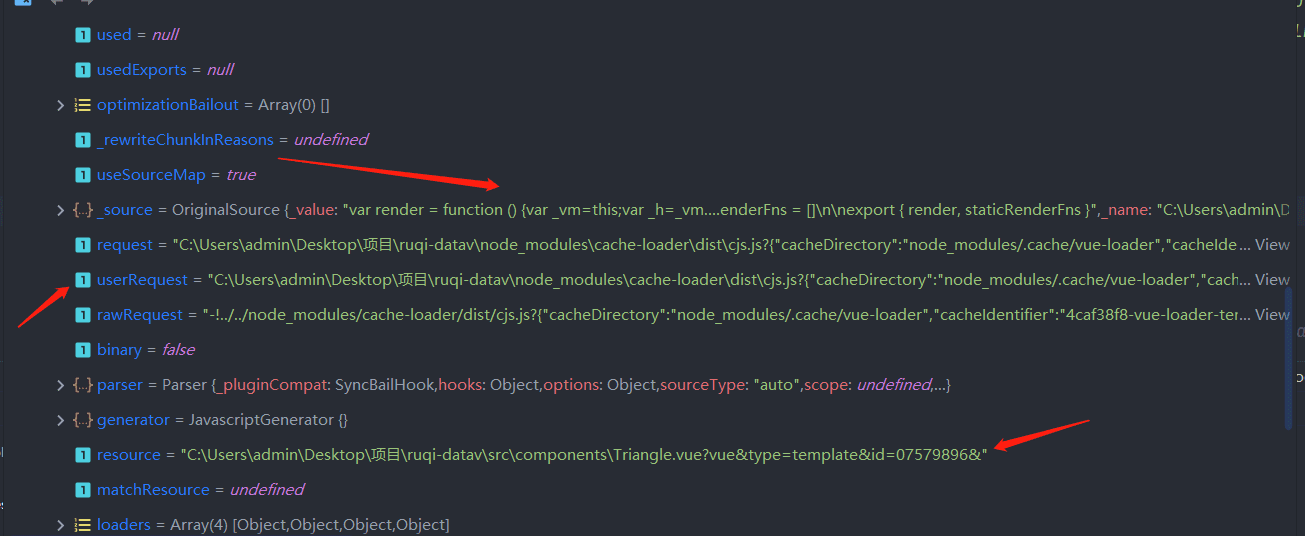
不难写出筛选出template渲染函数的代码:
// 判断是否vue模板 注意的是 mac的路径为相对路径 所以不能实例化的URL方法形式
// 改用正则
function isVueTemplate (url) {
if (/\.vue\?vue&type=template/.test(url)) {
return true
}
}
class CheckVueConflictPlugin {
private readonly options: CheckVueConflictPluginOptions;
constructor(options?: CheckVueConflictPluginOptions) {
this.options = options || {};
}
apply(compiler: Compiler) {
const { force = false } = this.options;
const pluginName = this.constructor.name;
const { options } = compiler;
const { mode } = options;
// 非生产模式并且不需要强制执行直接退出即可
if (mode !== 'production' && !force) {
return;
}
// 注册实例化compilation之后的钩子
compiler.hooks.compilation.tap(pluginName, (compilation) => {
compilation.hooks.seal.tap(pluginName, () => {
const newModule = Array.from(compilation.modules) as VueTemplateModule[];
const templateModulesArray = newModule.filter(
(module) => module.resource && isVueTemplate(module.resource) && module.resource !== module.userRequest,
);
// template模板有两种 一种是经过vue-loader模板处理的 template文件 这时候的request或者userRequest 引用路径其实就是vue-loader
// 一种是经过vue-loader编译之后导出的
// 我们要的是第儿2种即 经过vue-loader处理过后的 这时候的request与resource路径是不一样的
if (templateModulesArray.length) {
// 此时获取到的module模块内容就是经过vue-loader经过静态分析优化完的模板字符串内容
for (let i = 0; i < templateModulesArray.length; i++) {
if (templateModulesArray[i]._source._value) {
checkIsConflict(templateModulesArray[i]);
}
}
}
});
});
}
}
引入babel对template渲染函数进行ast语法树分析
从上面的步骤中我们获取到了经由vue-template-compilre编译优化过后的渲染字符串,假设原template的代码是这样子的:
<template>
<div id="app">
<router-view />
===============
<div>2131313</div>
<Triangle/>
<div>
<div>1</div>
<div>2</div>
<div>
<span>span1</span>
<span>span2</span>
<span>span3</span>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</template>经过vue-tempalte-compilre编译优化之后就会生成如下的渲染函数字符串(为了方便理解代码做了格式化以及注释):
// template中最终会被编译成render函数并且导出
var render = function() {
var _vm = this;
var _h = _vm.$createElement;
var _c = _vm._self._c || _h;
// 对于组件或者标签 会转化为_c函数
return _c(
"div",
{ attrs: { id: "app" } },
[
_c("router-view"),
// html的标签内容转化为_vm._v的函数形式
_vm._v("\n ===============\n "),
_c("div", [_vm._v("2131313")]),
_c("Triangle"),
_vm._m(0)
],
1
);
};
// 静态节点 vue中对于一些不会变化的节点会转化为静态节点,在diff的时候会跳过这些节点用于性能优化。
var staticRenderFns = [
function() {
var _vm = this;
var _h = _vm.$createElement;
var _c = _vm._self._c || _h;
return _c("div", [
_c("div", [_vm._v("1")]),
_c("div", [_vm._v("2")]),
_c("div", [
_c("span", [_vm._v("span1")]),
_c("span", [_vm._v("span2")]),
_c("span", [_vm._v("span3")])
])
]);
}
];
export {render, staticRenderFns}不难看出,为了检验模板中是否有遗留的合并冲突代码,我们只需要_vm._v中的字符串是进行正则匹配即可。我们把这段代码丢到astexplore中。
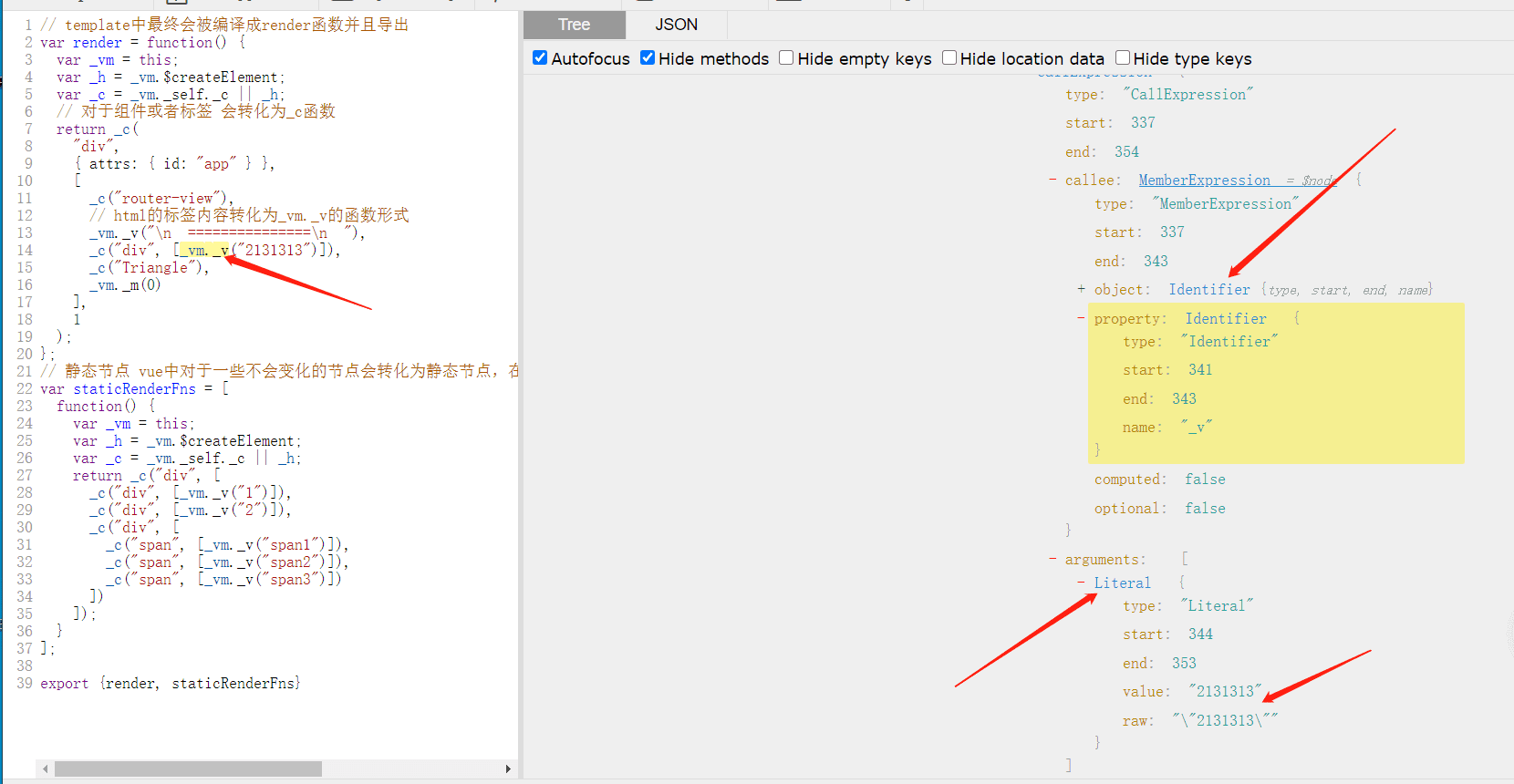
获取到相对应的ast语法树之后,通过babel插件把上面获取到的模板源文件转为为ast语法树,通过访问者模式判断特定的节点即可。
import { Compiler, Module } from 'webpack';
import { parse } from '@babel/parser';
import traverse from '@babel/traverse';
import * as babelTypes from '@babel/types';
import { StringLiteral } from '@babel/types';
interface VueTemplateModule extends Module {
resource?: string;
_source: {
_value: string;
};
userRequest?: string;
}
const newVueToken = ['_vm'];
const vuePropertyKey = ['_v'];
function checkIsConflict(module: VueTemplateModule) {
const { _source, resource } = module;
const vueTemplateAst = parse(_source._value, {
sourceType: 'module',
});
traverse(vueTemplateAst, {
CallExpression(path) {
const { callee } = path.node;
if (
!(
babelTypes.isMemberExpression(callee) &&
babelTypes.isIdentifier(callee.object) &&
newVueToken.includes(callee.object.name) &&
babelTypes.isIdentifier(callee.property) &&
vuePropertyKey.includes(callee.property.name)
)
) {
return;
}
// get the component type name and it's extra props options
const childrenArray = path.node.arguments;
const stringLiteralChildArray = childrenArray.filter((children) =>
babelTypes.isStringLiteral(children),
) as StringLiteral[];
const stringLiteralValArray = stringLiteralChildArray.map((child) => child.value);
const conflictText = stringLiteralValArray.find((strText) => strText.match(/(={7})|(>{7})|(<{7})/));
if (conflictText) {
// 检测到合并冲突 直接抛出错误
throw new Error(
`在 【${resource}】 文件中检测到疑似合并冲突,请处理完之后重新提交
出现合并冲突内容为${conflictText}
`,
);
}
},
});
}至此,一个检测vue渲染模板中是否有合并冲突代码的webpack插件就完成了,全部实现源码如下:
import { URL } from 'url';
import { Compiler, Module } from 'webpack';
import { parse } from '@babel/parser';
import traverse from '@babel/traverse';
import * as babelTypes from '@babel/types';
import { StringLiteral } from '@babel/types';
interface VueTemplateModule extends Module {
resource?: string;
_source: {
_value: string;
};
userRequest?: string;
}
interface CheckVueConflictPluginOptions {
// 是否强制开启进行模板冲突检测
force?: boolean;
}
const newVueToken = ['_vm'];
const vuePropertyKey = ['_v'];
// 判断是否vue模板 注意的是 mac的路径为相对路径 所以不能实例化的URL方法形式
// 改用正则
function isVueTemplate (url) {
if (/\.vue\?vue&type=template/.test(url)) {
return true
}
}
function checkIsConflict(module: VueTemplateModule) {
const { _source, resource } = module;
const vueTemplateAst = parse(_source._value, {
sourceType: 'module',
});
traverse(vueTemplateAst, {
CallExpression(path) {
const { callee } = path.node;
if (
!(
babelTypes.isMemberExpression(callee) &&
babelTypes.isIdentifier(callee.object) &&
newVueToken.includes(callee.object.name) &&
babelTypes.isIdentifier(callee.property) &&
vuePropertyKey.includes(callee.property.name)
)
) {
return;
}
// get the component type name and it's extra props options
const childrenArray = path.node.arguments;
const stringLiteralChildArray = childrenArray.filter((children) =>
babelTypes.isStringLiteral(children),
) as StringLiteral[];
const stringLiteralValArray = stringLiteralChildArray.map((child) => child.value);
const conflictText = stringLiteralValArray.find((strText) => strText.match(/(={7})|(>{7})|(<{7})/));
if (conflictText) {
// 检测到合并冲突 直接抛出错误
throw new Error(
`在 【${resource}】 文件中检测到疑似合并冲突,请处理完之后重新提交
出现合并冲突内容为${conflictText}
`,
);
}
},
});
}
class CheckVueConflictPlugin {
private readonly options: CheckVueConflictPluginOptions;
constructor(options?: CheckVueConflictPluginOptions) {
this.options = options || {};
}
apply(compiler: Compiler) {
const { force = false } = this.options;
const pluginName = this.constructor.name;
const { options } = compiler;
const { mode } = options;
// 非生产模式并且不需要强制执行直接退出即可
if (mode !== 'production' && !force) {
return;
}
// 注册实例化compilation之后的钩子
compiler.hooks.compilation.tap(pluginName, (compilation) => {
compilation.hooks.seal.tap(pluginName, () => {
const newModule = Array.from(compilation.modules) as VueTemplateModule[];
const templateModulesArray = newModule.filter(
(module) => module.resource && isVueTemplate(module.resource) && module.resource !== module.userRequest,
);
// template模板有两种 一种是经过vue-loader模板处理的 template文件 这时候的request或者userRequest 引用路径其实就是vue-loader
// 一种是经过vue-loader编译之后导出的
// 我们要的是第儿2种即 经过vue-loader处理过后的 这时候的request与resource路径是不一样的
if (templateModulesArray.length) {
// 此时获取到的module模块内容就是经过vue-loader经过静态分析优化完的模板字符串内容
for (let i = 0; i < templateModulesArray.length; i++) {
if (templateModulesArray[i]._source._value) {
checkIsConflict(templateModulesArray[i]);
}
}
}
});
});
}
}
export default CheckVueConflictPlugin;
加餐:vue3的兼容
vue3的单文件模板依然会分离成三个文件,通过type来区分(跟vue2一毛一样)
source.vue?vue&type=template表示渲染函数模板source.vue?vue&type=script表示script中的js逻辑source.vue?vue&type=style表示样式文件
只是编译的渲染模板发生了变化,如下面的template模板:
<template>
<header class="header">
<div class="logo">
<i class="back" />
</div>
<span>123456</span>
<div class="tabs">
<div class="tab-item" v-for="item in tabList" :key="item.name">
<RouterLink :to="item.link">{{ item.name }}</RouterLink>
</div>
</div>
==================
<RouterLink class="user" to="/user">
<i class="iconfont icon-user" />
>>>>>>>>>>>>sss
<span>测试环境数据</span>
</RouterLink>
</header>
</template>
会编译优化为如下的js代码:
import { createVNode as _createVNode, renderList as _renderList, Fragment as _Fragment, openBlock as _openBlock, createBlock as _createBlock, toDisplayString as _toDisplayString, createTextVNode as _createTextVNode, resolveComponent as _resolveComponent, withCtx as _withCtx, withScopeId as _withScopeId, pushScopeId as _pushScopeId, popScopeId as _popScopeId } from "vue"
const _withId = /*#__PURE__*/_withScopeId("data-v-77d8155b")
_pushScopeId("data-v-77d8155b")
const _hoisted_1 = { class: "header" }
const _hoisted_2 = /*#__PURE__*/_createVNode("div", { class: "logo" }, [
/*#__PURE__*/_createVNode("i", { class: "back" })
], -1)
const _hoisted_3 = /*#__PURE__*/_createVNode("span", null, "123456", -1)
const _hoisted_4 = { class: "tabs" }
const _hoisted_5 = /*#__PURE__*/_createTextVNode(" ================== ")
const _hoisted_6 = /*#__PURE__*/_createVNode("i", { class: "iconfont icon-user" }, null, -1)
const _hoisted_7 = /*#__PURE__*/_createTextVNode(" >>>>>>>>>>>>sss ")
const _hoisted_8 = /*#__PURE__*/_createVNode("span", null, "测试环境数据", -1)
_popScopeId()
export const render = /*#__PURE__*/_withId(function render(_ctx, _cache) {
const _component_RouterLink = _resolveComponent("RouterLink")
return (_openBlock(), _createBlock("header", _hoisted_1, [
_hoisted_2,
_hoisted_3,
_createVNode("div", _hoisted_4, [
(_openBlock(true), _createBlock(_Fragment, null, _renderList(_ctx.tabList, (item) => {
return (_openBlock(), _createBlock("div", {
class: "tab-item",
key: item.name
}, [
_createVNode(_component_RouterLink, {
to: item.link
}, {
default: _withId(() => [
_createTextVNode(_toDisplayString(item.name), 1 /* TEXT */)
]),
_: 2
}, 1032, ["to"])
]))
}), 128 /* KEYED_FRAGMENT */))
]),
_hoisted_5,
_createVNode(_component_RouterLink, {
class: "user",
to: "/user"
}, {
default: _withId(() => [
_hoisted_6,
_hoisted_7,
_hoisted_8
]),
_: 1
})
]))
})不难看出,获取静态文本的方法集中在_createVNode以及_createTextVNode这两个核心方法之中。根据相对应的ast语法树进行判断即可:
export function checkVue3IsConflict(module: VueTemplateModule) {
const { _source, resource } = module;
const vueTemplateAst = parse(_source._value, {
sourceType: 'module',
});
traverse(vueTemplateAst, {
CallExpression(path) {
// @ts-ignore
const { callee } = path.node;
const nodeArguments = path.node.arguments;
const isCreateVNode =
babelTypes.isIdentifier(callee) &&
callee.name === '_createVNode' &&
babelTypes.isStringLiteral(nodeArguments[2]);
const isCreateTextVNode =
babelTypes.isIdentifier(callee) &&
callee.name === '_createTextVNode' &&
babelTypes.isStringLiteral(nodeArguments[0]);
if (!(isCreateVNode || isCreateTextVNode)) {
return;
}
const pendingCheckStr = nodeArguments[isCreateVNode ? 2 : 0] as StringLiteral;
const conflictText = pendingCheckStr.value.match(/(={7})|(>{7})|(<{7})/);
if (conflictText) {
// 检测到合并冲突 直接抛出错误
throw new Error(
`在 【${resource}】 文件中检测到疑似合并冲突,请处理完之后重新提交
出现合并冲突内容为${pendingCheckStr.value}
`,
);
}
},
});
}
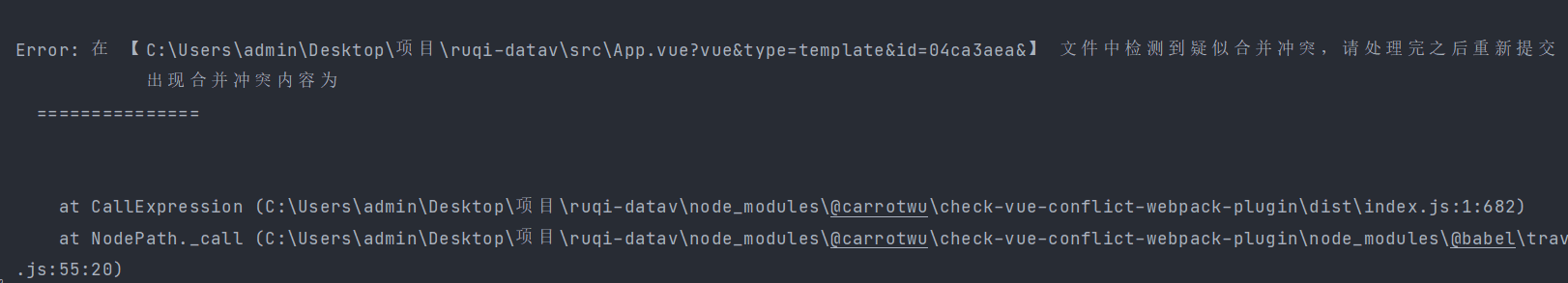
效果
使用
编写的库已上传到npm,有意向使用的话npm搜@carrotwu/check-vue-conflict-webpack-plugin即可